Justice’s scathing dissent slams high court ruling on illegal police stops
6/24/2016, 8:57 a.m.
Free Press wire reports
WASHINGTON
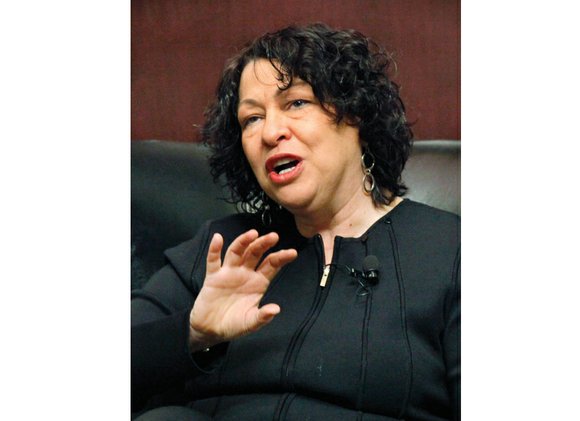
In a powerful dissent to a U.S. Supreme Court ruling that took an expansive view of the limits the Constitution places on police misconduct, Justice Sonia Sotomayor on Monday seemed to address the people most affected by unfortunate encounters with the police — black and brown Americans.
“Do not be soothed by the opinion’s technical language: This case allows the police to stop you on the street, demand your identification, and check it for outstanding traffic warrants — even if you are doing nothing wrong,” Justice Sotomayor wrote in the opening paragraph of her response to Utah v. Strieff, which the court decided in a 5-3 vote.
Justice Clarence Thomas wrote the majority opinion released Monday.
The case had asked the justices to decide whether evidence uncovered during an unlawful police stop could be used against the person in possession of it — a question that requires an interpretation of the Fourth Amendment‘s prohibitions against unreasonable searches and seizures.
It turns out that Edward Strieff, the Utah man at the center of the case, had been stopped by a police officer who had a hunch that Mr. Strieff was engaged in drug activity but didn’t have any real “reasonable suspicion” that he actually was, which is required by the Constitution for investigatory stops.
Or, as Justice Sotomayor put it: “In his search for lawbreaking, the officer in this case himself broke the law.”
But then the officer got lucky: When he ran Mr. Strieff’s driver’s license through his system, he noticed his suspect had a minor traffic warrant for an unpaid ticket. That meant the officer could hold Mr. Strieff and check him for contraband.
Then the officer got really lucky: He found methamphetamines in Mr. Strieff’s pocket, which provided a basis for an arrest and later charge of drug possession.
In his opinion, Justice Thomas decided that the drugs — the “poisonous fruit“ of the officer’s illegal stop — could be used against Mr. Strieff at his trial, even though the officer initially had violated Mr. Strieff’s rights.
He described the incident as the result of a couple of “at most negligent” mistakes on the officer’s part and downplayed its broader significance.
Justice Sotomayor wasn’t having any of this. And in an opinion joined by Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg, she questioned the premises of the majority — that “lawless police conduct” here was somehow uncommon or somehow not “systemic.”
“Respectfully, nothing about this case is isolated,” Justice Sotomayor wrote.
Justice Elena Kagan wrote a separate dissent noting that the majority’s approach “creates unfortunate incentives for the police.”
Displaying a keen understanding of the ongoing national conversation surrounding police brutality and abuse, Justice Sotomayor cited a broad range of examples of misconduct: The damning Department of Justice’s report on Ferguson, Mo.; studies on the prevalence of outstanding warrants and debt by criminal defendants; and the pattern of unconstitutional practices from numerous police departments, such as those in New York City, St. Louis and Newark, N.J.
In a section that wasn’t joined by Justice Ginsburg, Justice Sotomayor wrote “from my professional experiences” about the dire consequences faced by all the men and women who find themselves in the crosshairs of the criminal justice system.
One by one, she ran through instances of a Supreme Court all too willing to grant police more power to detain, arrest and search citizens — based on pretextual reasons, the way they look or even suspicion that they had broken a law that doesn’t exist.
She underscored that all bets are off once a person is caught in this system.
“Even if you are innocent, you will now join the 65 million Americans with an arrest record and experience the ‘civil death’ of discrimination by employers, landlords, and whoever else conducts a background check,” she continued.
Mr. Strieff may have been white, “but it is no secret that people of color are disproportionate victims of this type of scrutiny,” she added, citing “The New Jim Crow,” Michelle Alexander’s seminal book exploring the culture of the mass incarceration of black people in the United States.
Justice Sotomayor also referenced the writings of W.E.B. Du Bois, James Baldwin and Ta-Nehisi Coates — three black intellectuals from three different eras — to show how people of color have it harder than others and how things don’t seem to change.
“For generations, black and brown parents have given their children ‘the talk’ — instructing them never to run down the street; always keep your hands where they can be seen; do not even think of talking back to a stranger— all out of fear of how an officer with a gun will react to them,” Justice Sotomayor wrote.
“By legitimizing the conduct that produces this double consciousness, this case tells everyone, white and black, guilty and innocent, that an officer can verify your legal status at any time,” she wrote. “It says that your body is subject to invasion while courts excuse the violation of your rights. It implies that you are not a citizen of a democracy but the subject of a carceral state, just waiting to be cataloged.
“We must not pretend that the countless people who are routinely targeted by police are ‘isolated.’ They are the canaries in the coal mine whose deaths, civil and literal, warn us that no one can breathe in this atmosphere,” Justice Sotomayor wrote.
“They are the ones who recognize that unlawful police stops corrode all our civil liberties and threaten all our lives. Until their voices matter too, our justice system will continue to be anything but.”